
Breast cancer diagnosis by using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Since breast cancer can strike women without warning signs and symptoms, all women should be aware of screening and early detection of breast cancer. A number of clinical researches has indicated that early detection of breast cancer by using standard imaging approach –digital mammogram and breast ultrasound is essentially important as it is strongly associated with an increased number of available treatment options, increased survival with improved quality of life. Besides digital mammogram and breast ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging or shortly called MRI greatly helps to detect breast abnormalities. MRI uses radio waves and strong magnets to make detailed pictures of the inside of the breast, allowing doctors to visualize a variety of tumors in the breast, if there any. Although there is no definitive method of preventing breast cancer, early detection provides the best possible chance of effective treatment, especially if the earliest stage of breast cancer is found.
Importance of breast MRI
Breast MRI with dedicated breast coils uses strong magnets instead of radiation to make very detailed, cross-sectional pictures of the inside of the breast. Breast MRI scanner takes pictures from several angles in order to produce the imaging results with high level of accuracy. Breast MRI creates pictures of soft tissue parts that would sometimes be difficult to see when using other imaging tests. Benefits of breast MRI classified by different groups of patients include:
1.) For breast cancer screening: To screen for breast cancer, based on risk levels, women are grouped into:
High risk group: Women who fall into high risk group possess a lifetime risk of breast cancer of about 20%, or greater, compared to normal population. High risk is defined as below:
- Having first degree relatives diagnosed with breast cancer e.g. mother, grandmother, daughter and sibling with similar mother;
- Having genetic mutations of BRCA1 or BRCA2;
- Receiving previous radiation treatments to the chest when aged between 10-30; and
- Being diagnosed with certain diseases that increase chances of developing breast cancer e.g. Li-Fraumeni Syndrome, Cowden Syndrome or Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome.
Recommendations for high risk group: For women at high risk for breast cancer, a screening MRI is highly recommended along with a yearly mammogram, staring at age 25-30.
- Intermediate risk group: Women with intermediate risk have a lifetime risk of breast cancer of about 15-20%, compared to normal population. Women with intermediate risk refer to:
- Patients wish previous diagnosis of abnormal breast cells such as Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia (ADH) and Lobular Carcinoma in Situ ( LCIS).
- Patients who have had previous treatment of breast cancer and mammogram results shown dense breast tissue.
Recommendations for intermediate risk group: For women at intermediate risk for breast cancer, MRI is recommended once a year.
- Low risk group: Women with low risk have a lifetime risk of breast cancer less than 15%, compared to normal population.
Recommendations for low risk group: MRI is not recommended as a screening test for women at low risk of breast cancer.
2.) Preoperative evaluation of breast cancer: In patients who are diagnosed with breast cancer, breast MRI is used to evaluate:
- The extension of disease and tumor burden before breast conservative surgery is considered.
- The presence of two or more physically separate neoplasms in the same breast, technically called multifocal-multicentric tumors of the breast (MMBC).
- The presence of two (or more) primary breast cancers that occur in another breast at the same time (synchronous breast cancers).
3.) Determination of breast implant integrity: Breast MRI is used to determine breast implant integrity in women who underwent breast augmentation either with silicone implant or injection.
4.) Postoperative patients with recurrent breast cancer or positive surgical margin, defined as cancer cells are present at the edge of the resection specimen.
5.) Evaluation of treatment response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy – the administration of therapeutic agents before surgery.
6.) Investigation of breast cancer with metastasis to lymphatic system or other adjacent organs.
7.) Investigation of suspected mass that could not be clearly visualized by mammogram and breast ultrasound.
8.) MRI-guided breast biopsy: MRI-guided breast biopsy helps to locate a breast lump or abnormality and guide a needle to remove a tissue sample for examination under a microscope.
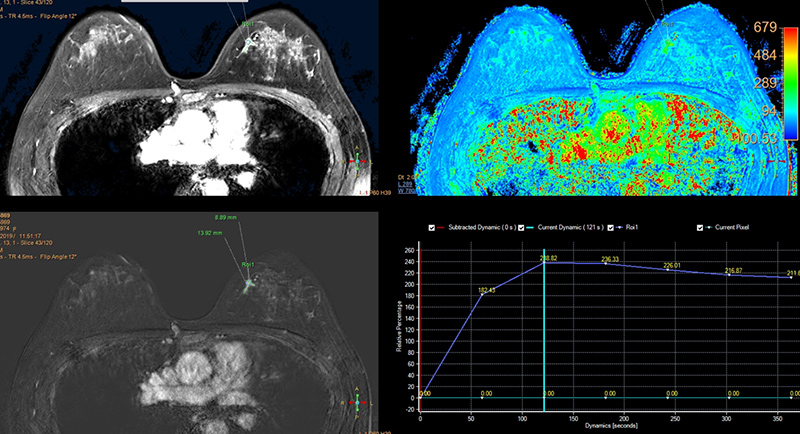
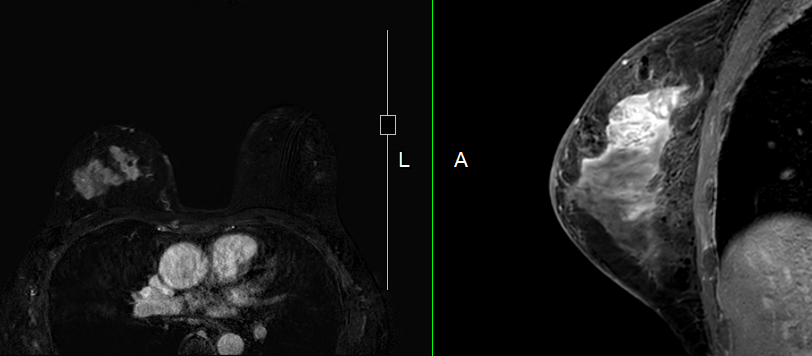
Getting ready for breast MRI test
MRI scans are usually done on an outpatient basis. During the test, patients will lie face down on a narrow, flat table. The breasts will hang down into an opening in the table so they can be scanned without being compressed. The test is painless. Patients may be asked to hold their breath or keep very still during certain parts of the test. Tips about breast MRI include:
- Since hormonal fluctuations can interfere with the accuracy of the test, leading to false positive, the most appropriate time to get breast MRI test in patients with fertile age is after the menstruation 7-14 days, counting from the first day of last period. However, in post-menopause patients, no restriction is needed.
- The most useful MRI exams for breast imaging use a contrast material called gadolinium. This contrast material will be injected into a vein in the arm before or during the exam, which helps to clearly show breast tissue details. Gadolinium-containing contrast agents may increase the risk of a rare but serious disease called nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in patients with severe kidney failure. Prior to injection, blood test to determine serum creatinine indicating kidney function (presented as eGFR) is required. If kidney function is impaired with eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73m2, injection of gadolinium-containing contrast agents must be avoided, unless benefits weighs greater than risks and close monitoring is highly needed. In addition, if patients have previous history of any kind of allergies with any contrast or dye, special care is vitally required.
- Breast MRI is recommended after breast surgery at least 1 month in order to reduce postoperative enhancement at the surgical site.
- Medical history including previous diagnosis and treatments must be clearly informed before conducting the test.
- Metallic substances can cause undesired reaction during MRI test such as severe burn. Patients must keep medical staff informed if they have any form of metallic implants or foreign material such as thread lifting for aesthetic purpose, tattoo, lodged or embedded bullets and metallic objects.
Instruction for preparation before testing
- Food and drink restriction is not required before having a test.
- Blood test to determine kidney function will be taken prior to running a test.
- Consent form needs to be signed by either patients or relatives.
- Changing outfit to hospital’s clothes before testing is required.
- Wearing mascara and/or eye shadow are not allowed since there might be metal contamination which interferes the results.
- Since magnetic resonance imaging scanner applies a very strong magnetic field, all kinds of metal objects must be kept away from the testing area. Previous history of surgery that involves metallic implants e.g. total knee replacement and cardiac pacemaker insertion need to be thoroughly screened. Metal subjects are strictly instructed to be stored in the lockers such as ATM and credit cards, hair clippers, dental work such as dentures or false teeth and dental braces, jewelry and accessories, body piercing, watches, wallets and USB.
- Before procedure begins, contrast agent will be administered intravenously.
- During the test, patients will lie face down on a narrow, flat table. The breasts will hang down into an opening in the table so they can be scanned without being compressed. The table then slides into a long, narrow tube which looks similar to a tunnel. During scanning, patients have to lie still inside the narrow tube. Patients may be asked to hold their breath or keep very still during certain parts of the test. The machine may make loud, clicking and whirring noises, as the magnet switches on and off. Patients need to follow instructions throughout the test.
- Earplugs or headphones are given to help block noise out during testing.
- During a test, patients might feel warm and sweat which is normal. However, if abnormal signs including breathing difficulties, shortness of breath, chest pain or tightness and skin rash present, it must be immediately informed to MRI technicians.
Special precautions of breast MRI
- Breast MRI is most often done while patients are lying on their belly inside a long, narrow tube. If patients have trouble with enclosed spaces or claustrophobia, additional medical advices are needed. In some cases, relaxing pills might be additionally prescribed.
- All metal objects must be removed before scanning. MRI must be avoided in patients who have carried metallic implants e.g. Automatic Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (AICD) or pacemaker, artificial cardiac valve, cerebral aneurysm clips, cochlear (ear) implant and metal coils inside blood vessels.
- In patients who underwent certain procedures involving metal plates, hip and knee replacement and cardiac stents, medical recommendation on MRI compatibility and safety must be provided before the test begins.
- MRI is strongly prohibited in pregnant patients, especially in the first trimester.
- Breastfeeding patients must be monitored under close supervision of the specialists. Breastfeeding should be temporarily stopped 24 hours after the scanning since contrast agent might enter breast milk. Breast pumping is needed before scanning.
Early detection and diagnosis of breast cancer help detecting breast cancer at its earliest stages, therefore the chances for successful treatment significantly increase. To screen and detect breast cancer effectively, breast MRI is highly recommended in high risk patients. In addition, breast MRI helps to differentiate benign and cancerous cells as well as monitor the treatment outcomes and breast cancer recurrence. Nevertheless, not every woman needs a breast MRI. Whether or not to take this test, it must be advised individually by expert specialists.